Sri Lanka has many benefits and incentives to offer to the global buyers and investors, apart from its close proximity to growing markets, and a dextrous and a capable workforce. Ours is a story of development and success in many ways. After a rocky start, the country has emerged ahead of many of our South Asian neighbours in the context of financial, human and social development.
The country has shown steady economic growth for the decade, graduating into a middle-income country with an average economic growth of over 5% and is in the process of evolving from a primarily rural-based economy to an urbanized economy based on manufacturing and services
Investment risks are an inherent factor to any location or a country, yet Sri Lanka has one of the best rising economies with the stars aligned in its favour.
With investment and export development policies that have been specially adapted to meet national development goals, the country is an ideal investment and sourcing destination for global buyers and investors.
The country has simplified taxation law while introducing new incentives for investors. and global buyers. Although the standard corporate income tax rate is at 28%, Sri Lanka provides for a reduced rate of 14% for specific sectors such as SMEs, Exports of Goods and Services, IT, Education, Tourism and Agriculture. Enhanced investment allowance has been offered to investors for their fixed capital investment over and above the normal depreciation.
Moreover, Sri Lanka has also entered into Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements with 44 countries at present.
Sri Lanka also maintains a liberal foreign exchange regime. Foreign exchange controls have been greatly liberalized enabling global investors and buyers to directly deal with local banks for their transaction excluding few instances where Central Bank approval is specifically needed. Free flow of currency transfer is allowed through Inward and Outward Investment Accounts.
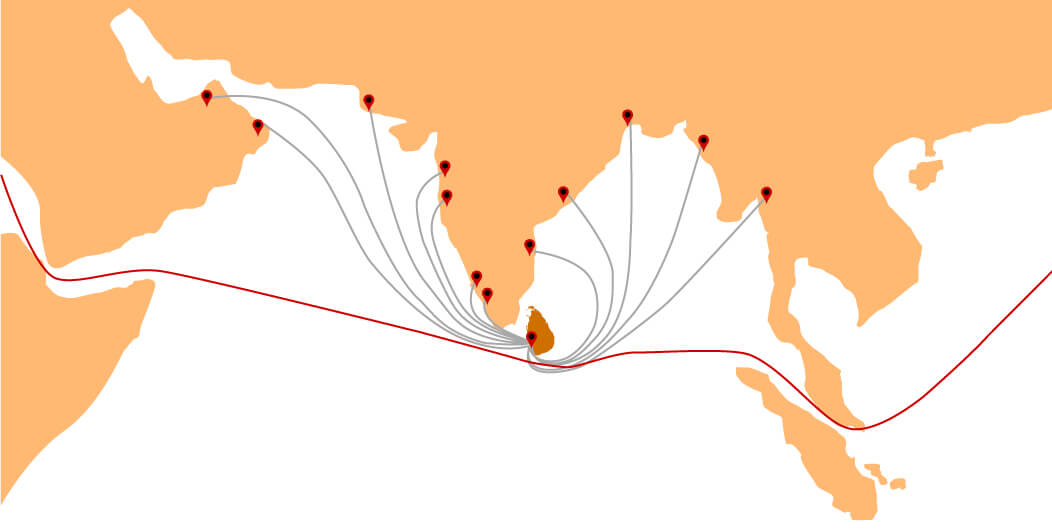
Situated in the centre of maritime trade routes that connect South Asia with the Far East, the Middle East, Africa, Australasia, Europe and America, Sri Lanka is a logistic hub for many shipping lines and airfreight services.
The country’s close proximity to the Indian subcontinent, our free trade agreements with South Asian countries under SAFTA, free trade agreements with Singapore, and the country’s participation in the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) had enabled the country to develop robust transhipment and entrepot hub centred around the shipping and airports in Colombo and Hambantota.
In addition, Free Ports and Bonded Areas have been set up at Sri Lanka’s major shipping and airports to facilitate Sri Lanka's import and export of goods and services with freedom to carry out transactions in convertible foreign currency.
An Educated and well-adopted workforce is one of Sri Lanka’s most abundant and significant resources. With a literacy that is one of the best in the region and is in par with developed countries in the world, mainly thanks to free education and compulsory schooling regulations, Sri Lanka has made headway in youth employment.
The country provides comprehensive tertiary education and vocational training through a network of public and private institutes, and Sri Lankan workforce excels in providing services that are intricate, nimble and sophisticated like in the case of ICT, light engineering services and electronic services.
Sri Lanka boasts of a widespread infrastructure facility, mainly due to the accelerated development programs launched by the government following the country’s emergence from a three-decade-long war.
Sri Lanka has an extensive road network amounting to over 100,000 km and a rail network consisting of about 1,944 km linking Colombo with the rest of the country. A network of newly developed expressways have enhanced the connectivity between Western, Southern, North Central and Central Provinces, while a road project is underway to improve the access to the Northern peninsular.
The telecommunication infrastructure in Sri Lanka has made great strides during the last six years, gaining a mobile penetration level of over 130% and a mobile broadband penetration level of 21%. The consistent development in the telecommunication infrastructure has enabled the country to make a market movement towards the introduction of 5G technology, and increase the use of e-commerce and e-banking methods in public and private transactions.
The country also has 12 Export Processing Zones already operating under the Board of Investment (BOI) in Sri Lanka, which provides a range of services including;